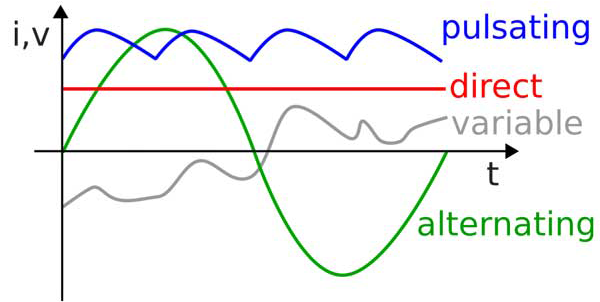
What is the difference between AC and DC?
Electrical current flows from a point of positive charge to a point of negative charge whilst essentially the electrons flow in the opposite direction.
AC stands for an alternating current. Essentially the polarity of the supply is changing with time and as it does the current flows in one direction and then the other. Mains power generation is typically AC - most generators are based on an alternator which creates an alternating current as the wire stator turns within a magnetic field. AC power transmission is also preferred for high voltage mains transmission because it is relatively easy to step down the voltages for various applications with transformers. The frequency of this alternating direction for mains supply in the UK is 50Hz, or 50 cycles per second.
DC stands for direct current. Here the current flow is in the one direction only and does not alternate. This is typical of the sort of current produced by a battery. Power generated by photovoltaic panels is DC and would need to be converted with a power inverter to be used for standard mains applications. DC power, once generated, is very useful in speed control motors etc.
IEC 60228 standard details requirements for Conductors of insulated cables, and these are all for Copper or Aluminium conductors in the form of solid (class 1), stranded (class 2) or flexible (class 5 or 6). Regardless of material or class, there is a maximum conductor resistance that each size of conductor is required to comply with. This requirement is a DC resistance requirement. There are however, differences in resistance when the circuit is DC as compared to AC.
The AC resistance of a conductor is always higher than the DC resistance and this can be attributed to two phenomena - skin effect and proximity effect.
Skin effect is essentially related to how frequency impacts the flow of current, with higher frequency current being more concentrated around the outside or skin of the conductor. At very high frequencies, often hollow conductors are used. At power frequencies (50-60Hz), whilst not so obvious, the change in resistance due to skin effect is still measurable.
On the other hand, proximity effect is related to the magnetic fields created by conductors in close proximity to one another. The physical arrangement of the conductors has an impact on the distribution of the magnetic field which is generally not even. The proximity effect is observed when the current carrying conductor is within the effect of flux of another current carrying conductor. When a current carrying conductor is within the vicinity of another conductor, its resistance is effectively increased because of the effect of flux from the other conductor.
People also ask
Electric cables work by providing a low resistance path for the current to flow through. Electric cables consist of a metal wire or core offering good conductivity such as copper or aluminium...
Two conductors which are separated by a distance can store an electric charge between them. A cable or harness with two or more wires can also store a charge and this can affect the way the cable performs...
The voltage rating of a cable is the highest voltage that may be continuously applied to a cable construction in compliance with the relevant cable standard or specification...
Cable Portfolio
View our comprehensive range of power, data, control and instrumentation cables and accessories
Go